The Wayamba Province of Sri Lanka is one of the nine provinces of Sri Lanka and consists of two administrative districts viz; Kurunegala and Puttalam. The province has a population of 2,370,075 (2011 census).
The province is known mainly for its numerous coconut plantations. Fishing, prawn farming and rubber tree plantations are other prominent industries of the region.
Paddy is the main agricultural crop in the province. Wayamba is the third largest paddy-producing area in Sri Lanka. Wayamba has a highly developed agricultural economy, growing a variety of fruits and vegetables, flowering plants, spices, oil-seeds in addition to the traditional plantation crops such as Coconut, Rubber and Rice. Rich soils and varied climate give Wayamba a potential for growing of virtually any crop.
It has a total land area of 7,972.6 sq.km of which 370.88 sq.km are in land water bodies. Water bodies include the lagoons, bays, freshwater tanks and streams in the area. With regard to land utilization, the province has 302,141.2 Ha of agricultural land (60.3 % of the land area of the province). (Source: District Statistical hand Book, 2019)
The coastal line of 240 km extends from Waikkal at its Wayamba end to Dutch Bay in the Puttalam district at its northern boundary.
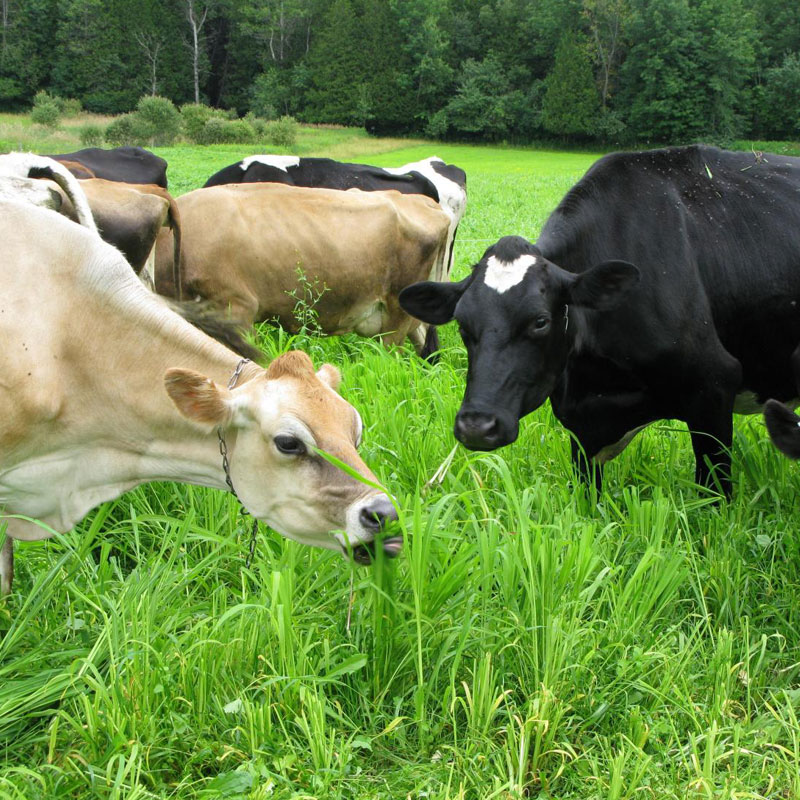

Overview of Agriculture Sector of Wayamba Province
(Including Livestock & Fisheries)
Agriculture Sector
The Agriculture sector is the dominant productive sector contributing much in the economy of the Province as 66 % of the total population involve in agriculture and its related activities for their livelihood, resulting in rapid development of the agriculture sector in the Province. Coconut which is the dominant and important plantation in the province and it is 37% of the land area of the province.
Fisheries Sector
Fisheries sector is another important productive sector of the province. Existing long coastal shoreline (16 % of total coastal line of the island) of the province contributes to marine fishing activities, giving opportunities to the fishing community to involve in fishing related activities including export of fish products. There are around 31,642 active marine and inland fishermen deploying over 8,469 fishing boats of various types and 910 inland fishing boats. In Wayamba Province, inland fishing contributes 12 % of national inland fish production while marine fishing contributes 15 % of the national marine fish production.
Livestock Sector
The livestock Industry has become an important sector for entrepreneurs in the Wayamba Province as this province is one of the major milk producing regions in Sri Lanka. Milk production reached closed to around 6,259,000 Liters in 2018 and the egg production reached 138 Mn per month in 2019. Given below are some vital statics of the livestock sector of Wayamba Province.
According to 2018 Annual Report of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka, the livestock sector contributes 0.6 % to GDP. According to the Department of Animal Production & Health year 2019 statistical information, Wayamba Provincial cattle population was 209,946. Buffalo population was 32,890. Provincial goat population was 73,742. Provincial swine population was 37,602. Comparing the milk production with other provinces in the country, Wayamba Province holds 2nd place by producing 81 Mn Liters milk in year 2018. As a Province, in year 2018, Wayamba Provincial annual milk production of cow milk was 66 Mn Liters and buffalo milk 15 Mn Liters and its contribution to the national milk production was 17 %. The provincial milk production has been increasing during the last few years by means of 159,000 Liters per day in 2014 to around 200,000 Liters per day in 2019.


Technology Application Priorities of Wayamba Province.
Given below is the summary of technology application priorities of the Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries sub sectors of the Wayamba Province.
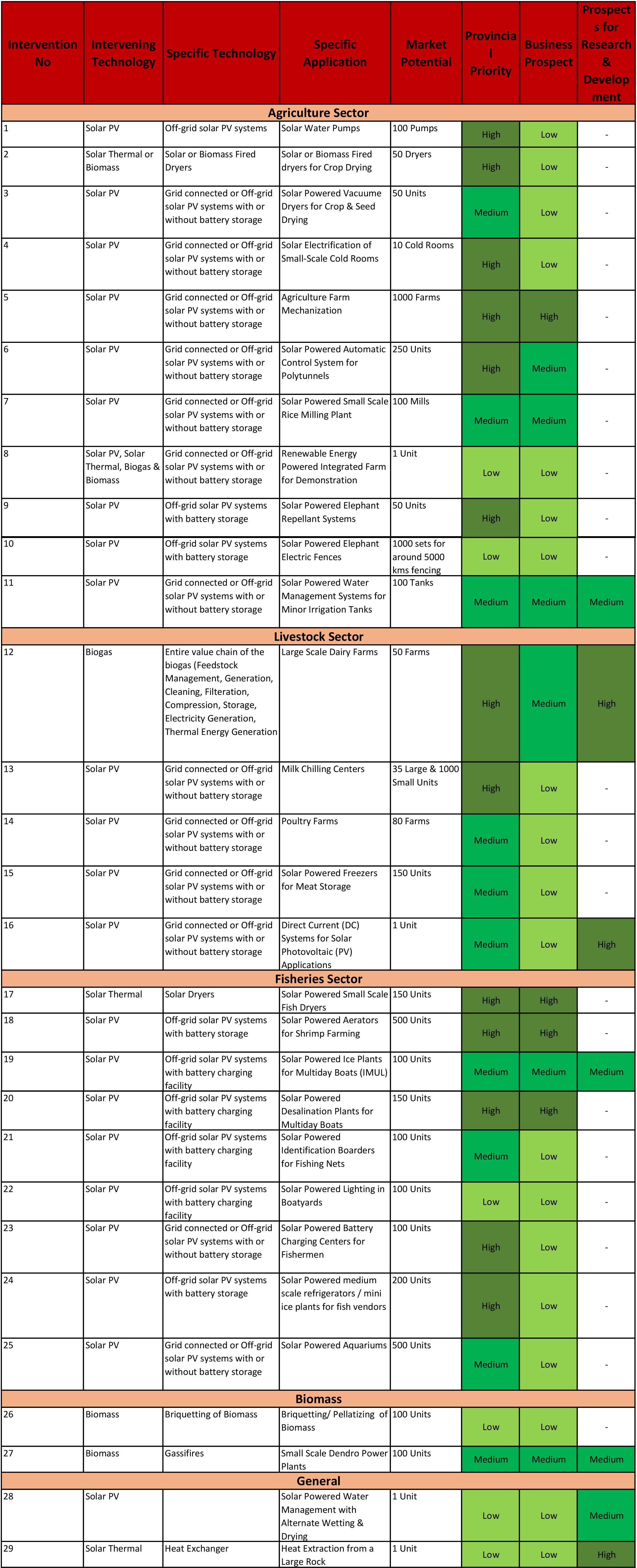
Twenty-nine (29) technology applications have been identified for the consideration of the TSSC Project and they are listed in the above table. Provincial priorities are indicated under three levels; “High”, “Medium” and “Low”. Applications having high prospects for business development and high prospects for further research and development also have been identified and marked as “high”.

